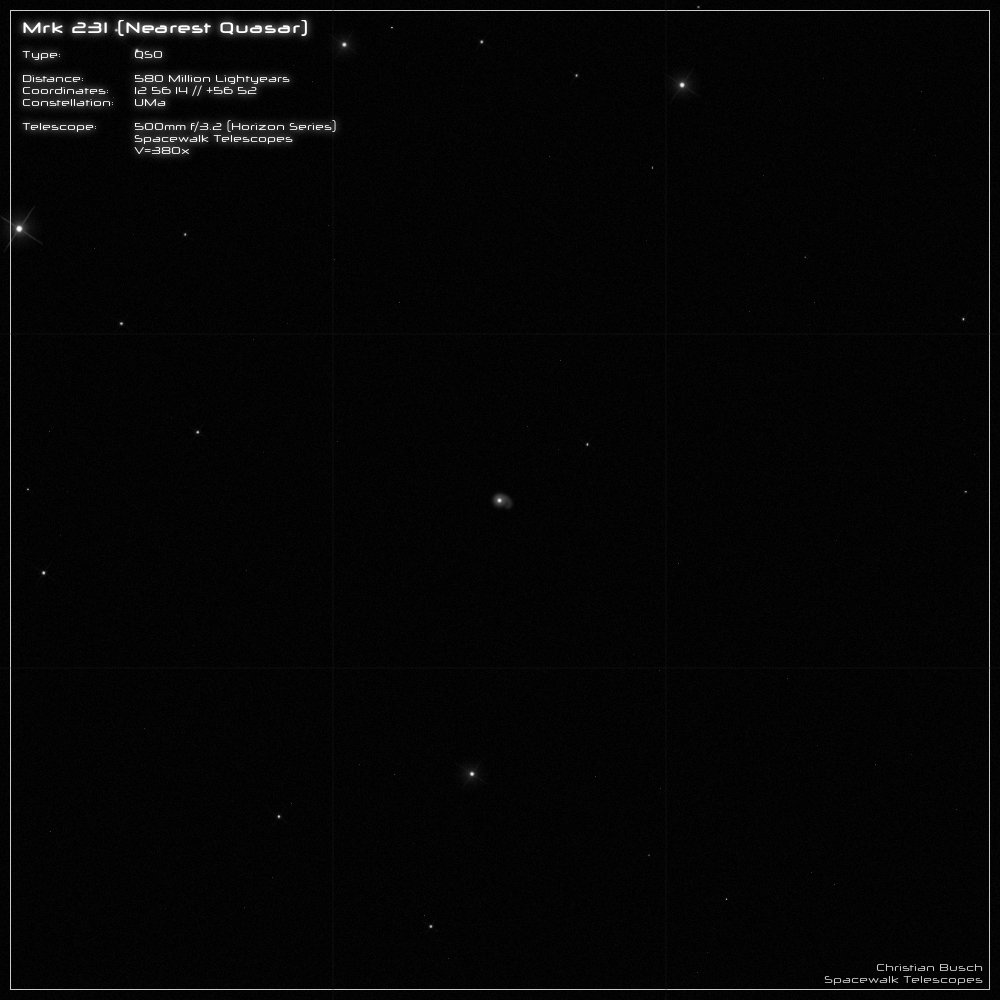
Markarian 231 - QSO
Markarian 231 - or Mrk231 for short - is a type 1 Seyfert galaxy in the constellation of the Big Dipper (UMa), which was discovered and classified as such in 1969. It
has an apparent magnitude of 13.8mag and an extent of 0.4'x0.5' arcminutes. Its redshift is z= 0.042, which corresponds to a distance of around 580 million light-years.
Because of the expansion of the universe, Mrk 231 is moving away from us at a speed of v= 12,400 km/s.
The galaxy, with a diameter of around 85,000 light-years, has a starburst ring in which 100 solar masses are converted into stars every year. A supermassive black hole
of 150 million solar masses is thought to be in the active core, which is orbited every 1.2 years by another SMBH of 4 million solar masses. However, this theory has
not yet been confirmed.
The absolute magnitude of the core can be determined as M = -22.4mag, which corresponds to a luminosity of almost 100 billion suns. This makes Mrk 231 the closest
quasar to us.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In my 20" telescope, Mrk 231 can be easily recognized as a stellar point even at a low magnification of 120x.
Things get really interesting at 380x. First of all, a round halo is noticeable around the bright, stellar core. On closer inspection, you can see that the halo is not uniform,
but has a kind of spiral arm moving outwards. Given the enormous distance, this is truly remarkable.
What I find particularly fascinating is the fact that quasars normally just appear as star-like points - but in the case of Mrk 231, even the host galaxy can be recognized. :))